Axis Ii of Dsm-iv Is Used to Describe
DSM-IV-TR Multiaxial Format Axis I. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis II Personality Disorders SCID-II.

Dsm Iv Axis System Dsm Iv Medical School Studying Practical Nursing
And Axis V was an assessment of.

. Axis II was reserved for personality disorders and mental retardation. Axis II personality disorders were based on the Chinese version of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis II Personality Disorders. Avoidant Personality Disorder 30182 Axis III.
Histrionic personality disorder paranoid personality disorder antisocial personality disorder. Besides in Europe there is also an International Classification of Diseases ICD-10. Diabetes High blood pressure hypertension High pressure in the arteries vessels that carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Personality disorders and mental retardation. Personality Disorders or Mental Retardation. Axis I consisted of mental health and substance use disorders SUDs.
Axis IV was used to describe psychosocial and environmental factors affecting the person. A total of 797 randomly selected psychiatrists and psychologists used the SWAP-200 to describe either an actual patient or a hypothetical prototypical patient with one of 14 personality disorders one of the 10 DSM-IV axis II disorders or one of four disorders included in the appendix or in DSM-III-R or a healthy high-functioning patient. Major Depressive Disorder Single Episode Severe without Psychotic Features with Atypical Features 29623 Physical Abuse of Adult V6112 Axis II.
Measure ethical decision making ability. First Gibbon Spitzer Williams Benjamin 1997 was developed to complement the widely used Axis I version of the SCID First Spitzer Gibbon Williams 1997The SCID-II has semi-structured format like the Axis I version but it covers the 10 standard DSM-IV Axis II personality. Axis IV was used to describe psychosocial and environmental factors affecting the person.
First one should assess the operating characteris-tics of axis II diagnoses treated both dimensionally and. Axis II was reserved for personality disorders and mental retardation. Three DSM-IV axis II clusters A B and C.
Problems with a primary support group. Axis II personality disorders and intellectual disabilities Axis III medical conditions Axis IV psychosocial and environmental factors Axis V global assessment of functioning Diagnostic codes In DSM-IV most disorders correspond with specific codes. The diagnostic system that was typically used to diagnose borderline personality disorder BPD and other personality disorders using axes are now obsolete.
Explore Axis IV of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Learn about environmental and psychosocial factors and how they are related to the treatment of mental disorders. Personality disorders and mental retardation including narcissistic personality disorder and avoidant personality. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders SCID-I is a diagnostic exam used to determine DSM-IV Axis I disorders major mental disordersThe SCID-II is a diagnostic exam used to determine Axis II disorders personality disordersThere are at least 700 published studies in which the SCID was the diagnostic instrument used.
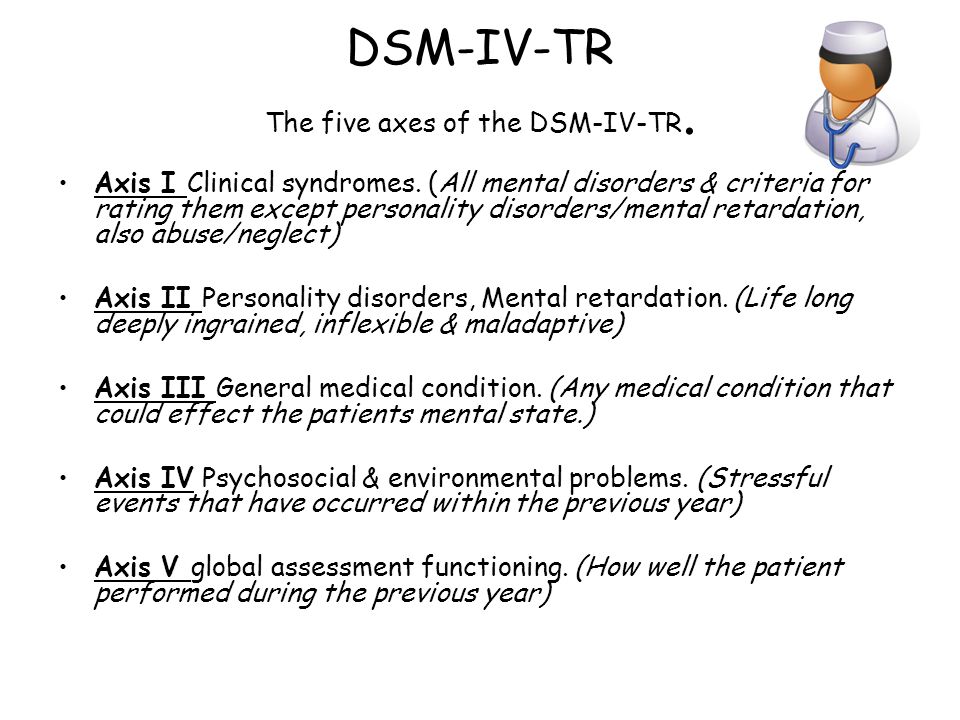
Longstanding personality traits may or may not be involved in development of Axis I disorder MENTAL RETARDATION. Axis IV was to note psychosocial and environmental problems eg housing employment. The five diagnostic axes specified by DSM-IV-TR are.
Axis I and Axis II disorders were assessed with the Composite International Diagnostic Interview CIDI and the Structured Interview for DSM-IV Personality SIDP-IV respectively. Axis III provided information about any medical conditions that were present which might impact the patients mental disorder or its management. 1-5 Axis I clinical psychiatric disorders ex.
DSM-IV SCID-IP32 adapted for use with proxy informants was administered by a psychiatrist to determine the presence or absence of current Axis I mental disorders. Contributing Environmental or Psychosocial Factors. Does DSM-5 have axis.
In the DSM-IV-TR the GAF scale is used to. Factors which might have been included here were. An Example of the Axis Scale Imagine that you are a clinician and a 50-year-old male client walks into your office and reports feeling extremely sad.
Stressors severe due to past psychiatric history and personality pathology as well as anxiety related symptoms. Assess overall functioning of the client. Medical or Physical Conditions.
Global Assessment of Functioning. Axis III was used for coding general medical conditions. Axis I consisted of mental health and substance use disorders SUDs.
Medical or Physical Conditions. Assess the cognitive functioning of the client. Global Assessment of Functioning.
Dimensional personality disorder scores constructed by correlating patients SWAP-200-A descriptions with prototypes of each DSM-IV axis II disorder correlated in expected and conceptually meaningful ways with other ways of assessing axis II disorders. BPD and other personality disorders were diagnosed as Axis II disorders in the last Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders fourth edition DSM-IV. Axis IV was to note psychosocial and environmental problems eg housing employment.
Clinical disorders such as panic disorder and bipolar disorder Axis II. And Axis V was an assessment of overall functioning known as the GAF. Borderline personality disorder Axis III General medical conditions ex.
Depression schizophreniaBipolar Axis II Personality disorders ex. Major parts of the SCID have. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were used to investigate the underlying structure of 25 disorders.
Axis III was used for coding general medical conditions. These and other considerations suggest that if one is to employ or develop a system for classifying adolescent per-sonality pathology one would do well to consider the fol-lowing. Problems with a primary support group Problems related to the social environment Educational problems Occupational problems Housing problems Economic problems Problems with access to health care services.
1 Factors which might have been included here were. With multiple measures of adaptive functioning such as measures of school and peer functioning and. Psychosocial and environmental problems.
-encompasses problematic ways of relating to world such as. Borderline personality disorder with history of self-mutilation which is stable at this time. Clinical disorders including anxiety disorders mood disorders schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders.
Contributing Environmental or Psychosocial Factors. Personality Disorders or Mental Retardation. What is the drug of choice for anxiety.
Dsm Iv To Dsm 5 Changes Overview Dsm 5 Changes Ncbi Bookshelf
Classification Of Mental Disorders Ppt Download

Comparison Of The Diagnostic Axes In Icd 10 And Dsm Iv Download Table

Dsm Iv Classification System Presented By Ppt Video Online Download

Introduction To Psychopathology Dsm Iv Therapy Worksheets Global Assessment Of Functioning

Ppt Structure Of The Dsm Iv Tr 5 Axes Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3128913

Dsm Iv Diagnosis Scoring Guide For Axis I And Axis Iii Download Table

Axis I En Axis Ii Diagnosis According To Dsm Iv Classification For The Download Table

17 The Dsm Iv Tr A Multiaxial System For Psychiatric Diagnosis Clinical Gate
Comments
Post a Comment